Get Expert Advice from Top Surgeons! Schedule Your Consultation.
Get The Best Diabetes Treatment At GEM Hospital
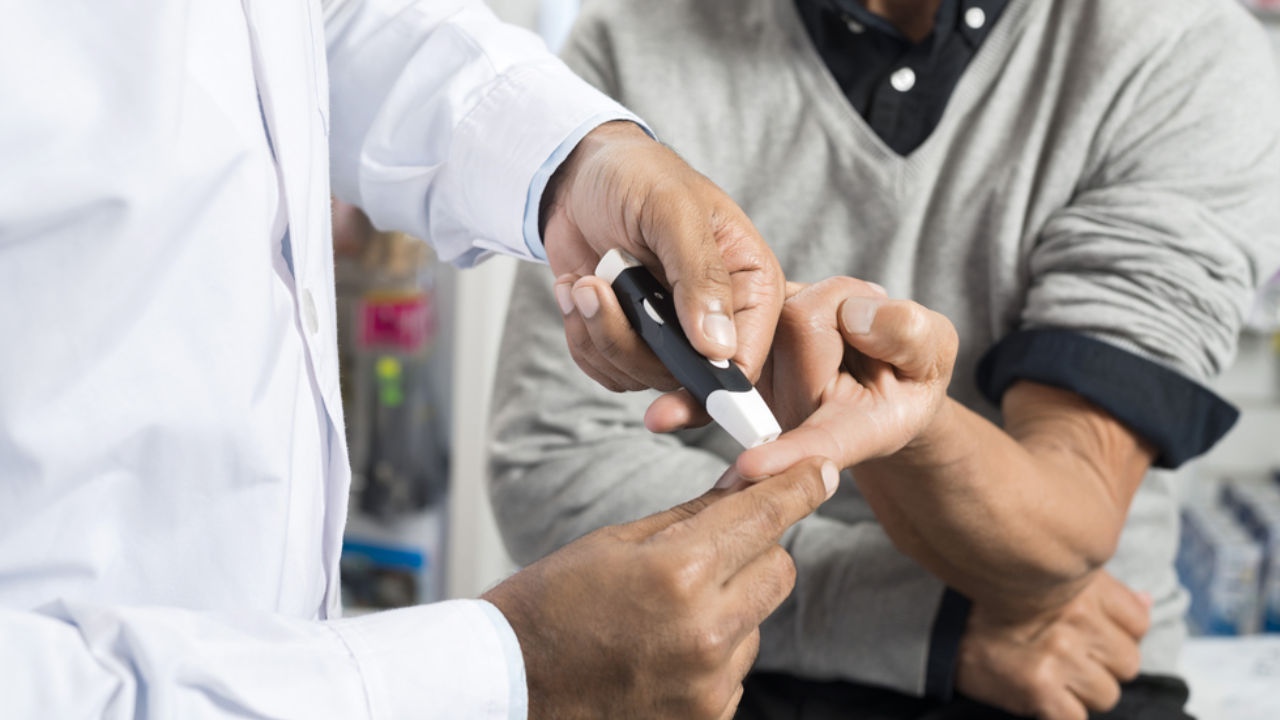
Providing advanced diabetes treatment with a focus on personalized care, our expert team at GEM Hospital is dedicated to effectively managing and treating diabetes. With a commitment to improving health and enhancing quality of life, we offer comprehensive and specialized care tailored to meet individual needs, ensuring the best outcomes for our patients.
-
Trusted Expertise
-
Precise Diagnostics
-
Advanced Treatments
-
Quality Care
-
24/7 Assistance
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes, often referred to as diabetes mellitus by medical professionals, is a chronic disease that affects the way your body regulates blood sugar, or glucose. Glucose is vital because it's a primary energy source for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. It's also your brain's main source of fuel. However, having too much glucose in your blood can lead to health problems, which necessitate diabetes treatment.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is mainly categorized into three types, each with unique causes and treatment strategies:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the body mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin daily to survive. This type is often diagnosed in children and young adults.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form of diabetes, Type 2, occurs when your body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin. It's most often diagnosed in adults but is increasingly seen in children, adolescents, and younger adults due to rising obesity rates.Effective diabetes treatment is crucial for managing this condition
-
Gestational Diabetes: This type develops in some women during pregnancy. It usually disappears after giving birth, but it can significantly increase the mother's risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset diabetes or T2D, is a chronic disease that affects the way your body processes blood sugar (glucose). It is a form of diabetes mellitus and is characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood due to insulin resistance. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the body fails to produce sufficient insulin, Type 2 diabetes develops over time and is largely the result of body cells not responding properly to insulin. Proper diabetes treatment is essential to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The exact causes of Type 2 diabetes are not completely understood, but several factors are known to increase the risk. These include genetics, lack of exercise, being overweight, and having an unhealthy diet. Insulin resistance is a key feature of Type 2 diabetes, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes develop slowly, and many people might not notice them until the condition has progressed significantly. Common symptoms include:
-
Increased thirst and frequent urination.
-
Extreme fatigue.
-
Blurred vision.
-
Slow healing of cuts and bruises.
-
Tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands or feet.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 diabetes involves monitoring blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and sometimes, diabetes medications or insulin therapy. It is crucial to maintain blood sugar levels within your target range to avoid complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart problems.
Diet and Exercise
A healthy diet and regular exercise are vital for managing blood sugar levels. The type 2 diabetes diet should include plenty of non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, and high-fiber foods. Regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently, an important aspect of diabetes treatment.
Medication and Monitoring
Many people with Type 2 diabetes need medication to help manage their blood sugar levels. Diabetes monitoring devices are also essential for keeping track of your blood sugar levels regularly, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Treatment aims to manage the condition effectively and prevent complications. This includes not only lifestyle adjustments but also possibly diabetes medication or insulin therapy. New treatments for Type 2 diabetes continue to be developed, offering hope for easier and more effective management of the condition.
Complications and Care
Without proper management, Type 2 diabetes can lead to a host of health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetic neuropathy, and renal problems. Comprehensive diabetes treatment is essential and should include regular medical check-ups to monitor the health conditions that can arise from living with diabetes.
Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes
Diagnosing Type 2 diabetes is a critical step in managing and treating the disease effectively. Early detection can help prevent complications and improve quality of life. Here’s what you need to know about the process of diagnosing Type 2 diabetes and how diabetes treatment can make a significant difference.
Blood Tests Used in Diagnosis
Several blood tests are utilized to diagnose Type 2 diabetes:
-
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG): This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. A level of 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): The OGTT involves fasting overnight followed by fasting blood sugar measurement. Then, you'll drink a sugary solution, and your blood sugar levels will be tested periodically for the next two hours. A blood sugar level less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) is normal, a reading between 140 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L) indicates prediabetes, and a level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher after two hours suggests diabetes.
-
Hemoglobin A1c Test: This test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes. An A1c between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered prediabetes, and a level less than 5.7% is normal. Regular A1c testing is essential in monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes treatment.
-
Random Blood Sugar Test: A blood sample will be taken at a random time, regardless of when you last ate. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes, especially if accompanied by symptoms of high blood sugar.
Additional Tests: In some cases, additional tests may be recommended to rule out other conditions or to assess the presence of complications related to diabetes, such as high cholesterol or high blood pressure.
Treatment and Management of Diabetes
Effective treatment and management of diabetes are crucial for maintaining quality of life and preventing complications associated with the disease. Whether you have been recently diagnosed or are looking to optimize your current management plan, understanding comprehensive approaches to diabetes treatment can make a significant difference. Here are the key aspects of diabetes management:
Medical Treatments
Medical treatment for diabetes primarily aims to maintain blood glucose levels within a target range to prevent or delay complications.
Medications: For many people with Type 2 diabetes, medications become a necessary part of daily life. These may include:
-
Metformin: Helps reduce glucose production in the liver.
-
Sulfonylureas: Increase pancreatic insulin production.
-
DPP-4 inhibitors: Moderate insulin production and decrease the amount of glucose made by the liver.
-
GLP-1 receptor agonists: Slow digestion and improve blood glucose levels.
-
SGLT2 inhibitors: Allow the kidneys to remove sugar from the body through urine.
-
Insulin therapy: Some people with Type 2 diabetes may need insulin, especially those who cannot maintain their blood glucose levels with other medications.
Advanced therapies: For more severe cases, especially in Type 1 diabetes, insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems can be life-changing, helping to maintain more consistent blood sugar levels and optimize diabetes treatment outcomes.
Lifestyle Management
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact the effectiveness of diabetes treatment and overall health outcomes.
Diet: Eating a balanced diet is crucial. Key recommendations include:
-
Choosing whole grains over processed carbohydrates.
-
Including a variety of fruits and vegetables.
-
Opting for lean proteins and avoiding trans fats.
-
Monitoring carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood glucose levels.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve blood glucose control, reduce cardiovascular risk, and promote overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly important in diabetes management. Weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Continuous monitoring and adjustments are required to keep diabetes under control and prevent complications.
-
Blood Glucose MonitoringRegular blood glucose monitoring is essential to understand how well your diabetes treatment plan is working. It provides immediate feedback and helps in making informed decisions about diet, activity, and medications.
-
HbA1c Tests The HbA1c test provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. It's a crucial tool for assessing long-term glycemic control. Most diabetes management plans aim for an HbA1c of less than 7%, but your doctor may customize this target based on your individual health.
-
Regular Check-UpsRegular visits to a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your overall health and making necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. These check-ups often include screening for diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
Prevention and Complications
Diabetes is a complex health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be managed effectively with proper treatment, preventing the onset of diabetes and understanding the potential complications are crucial steps in reducing its impact.
Preventing Diabetes
Preventing diabetes largely hinges on making informed lifestyle choices early in life. Even simple changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes, particularly for those predisposed to the condition due to genetic factors or other health issues.
Importance of Early Lifestyle Changes
-
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and regulate blood sugar levels. These habits are part of preventive diabetes treatment.
-
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity helps control weight, uses up glucose as energy, and makes cells more sensitive to insulin.
-
Weight Management: Being overweight is a significant risk factor for diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk.
-
Avoiding Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing diabetes
-
Regular Check-Ups: Regular health screenings can detect prediabetes, which can be managed before it develops into full-blown diabetes.
These proactive steps not only help prevent diabetes but also promote overall well-being and improve quality of life.
Potential Complications
Diabetes can lead to a host of complications if not managed properly. These complications can affect nearly every organ in the body and can lead to significant health problems, some of which can be life-threatening.
Short-Term Complications
-
Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar can occur suddenly and needs to be treated promptly to avoid serious consequences.
-
Hyperglycemia: High blood sugar, if persistent, can lead to complications like ketoacidosis, which is dangerous and potentially fatal.
Long-Term Complications
-
Cardiovascular Disease: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, and narrowing of arteries.
-
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood vessels that nourish your nerves, leading to tingling, numbness, burning, and pain that usually begins at the tips of the toes or fingers.
-
Kidney Damage (Nephropathy): Diabetes can damage the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease.
-
Eye Damage: Diabetes increases the risk of serious vision conditions, including cataracts, glaucoma, and the most severe, diabetic retinopathy.
-
Foot Damage: Nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow increases the risk of various foot complications. Left untreated, cuts and blisters can develop serious infections.
Why Choose GEM Hospital for Diabetes Care?
Choosing GEM Hospital for diabetes care means selecting a center of excellence that offers expert care, advanced treatment options, and a comprehensive approach to managing diabetes. At GEM Hospital, we are dedicated to providing our patients with the best possible care and improving their quality of life through effective diabetes treatment strategies. Whether you are newly diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, GEM Hospital is here to support you every step of the way.
Schedule Your Consultation Today
For those in need of comprehensive diabetes treatment, our specialized team at GEM Hospital is here to guide you every step of the way. Don’t wait to take control of your health—schedule a consultation with us today and start your path to better diabetes management and improved well-being.